Tracealyzer事件缓存读写实现与源码BUG修改
一.
前言
前面我们分享了
Tracealyzer
发送到上位机的事件数据的格式
,
这一篇继续分析事件是如何存储以及如何发送到上位机的,其实前面系统框图也已经介绍了,核心是使用了一个发送缓存区,事件触发点记录事件时先写缓存区,然后发送任务读缓存区数据进行发送,这一篇就来详细分析这个过程。
二.
发送缓存实现分析
我们先来画出整体的框图,如下图所示,绿色部分是缓存初始化部分,蓝色部分是任务读缓存发送部分,黄色部分是记录事件时写缓存部分,白色部分是缓存的数据结构。下面来分开介绍各个部分。
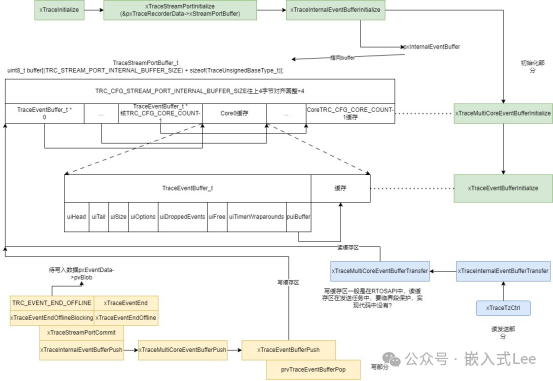
发送缓存的初始化与数据结构
前面框图看到绿色部分是缓存初始化过程
xTraceInitialize
时调用
xTraceStreamPortInitialize
(&pxTraceRecorderData->xStreamPortBuffer)
初始化缓存
,
而
pxTraceRecorderData
指向的是动态或者静态分配的一个全局大的结构体的指针,这个结构体记录所有的信息,其中
xStreamPortBuffer
就是用于发送的缓存。调用
xTraceInternalEventBufferInitialize
初始化时还会初始化
pxInternalEventBuffer
全局指针变量指向
xStreamPortBuffer
的缓存区。
typedef struct TraceStreamPortBuffer{uint8_t buffer[(TRC_STREAM_PORT_INTERNAL_BUFFER_SIZE) + sizeof(TraceUnsignedBaseType_t)];} TraceStreamPortBuffer_t;
对应如下红色框部分,整个缓存向上圆整为
4
字节对齐。

xTraceMultiCoreEventBufferInitialize
对应的是如下数据结构,初始化多核如何分配缓存,前面
TRC_CFG_CORE_COUNT
个指针对应
TRC_CFG_CORE_COUNT
个核,每个核指向后面一个缓存,实际就是整个缓存去掉前面的每个核的指针,剩余部分分配给每个核使用。
每个核心都有一个指针,且是连续的,根据索引就可以找到指定核的指针,然后根据剩余部分平分给各个缓存,就知道每个核指针指向的缓存位置。
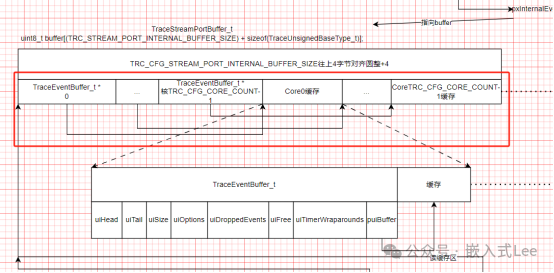
xTraceEventBufferInitialize
则初始化每个核自己的缓存,对应如下红色框部分,每个核自己的缓存继续
划
分为前面的信息头
TraceEventBuffer_t
用于管理缓存,和后面的有效缓存部分,其中
puiBuffer
指针即指向后面的有效缓存,事件信息就是存储在后面有效缓存部分,按照循环缓存形式由
TraceEventBuffer_t
进行管理。循环缓存的实现可以参考本公众号之前分享的
FIFO
相关的文章,核心思想就是有一个
uiHead
指针用于写地址记录,
uiTail
有一个读指针记录读地址。读地址追赶写地址,即消费者追赶生产者,这里
uiTail==uiHead
时表示空,单独使用一个位置表示满即
uiTail=uiHead+1
时表示满,与我们之前分享的单独使用一个记录有效数据的变量有点差别,本质是一样的,区分空满就是需要单独一个记录信息,要不使用一个成员变量要不使用一个缓存的位置。

typedef struct TraceEventBuffer{uint32_t uiHead; /**< Head index of buffer */uint32_t uiTail; /**< Tail index of buffer */uint32_t uiSize; /**< Buffer size */uint32_t uiOptions; /**< Options (skip/overwrite when full) */uint32_t uiDroppedEvents; /**< Nr of dropped events */uint32_t uiFree; /**< Nr of free bytes */uint32_t uiTimerWraparounds; /**< Nr of timer wraparounds */uint8_t* puiBuffer; /**< Trace Event Buffer: may be NULL */} TraceEventBuffer_t;
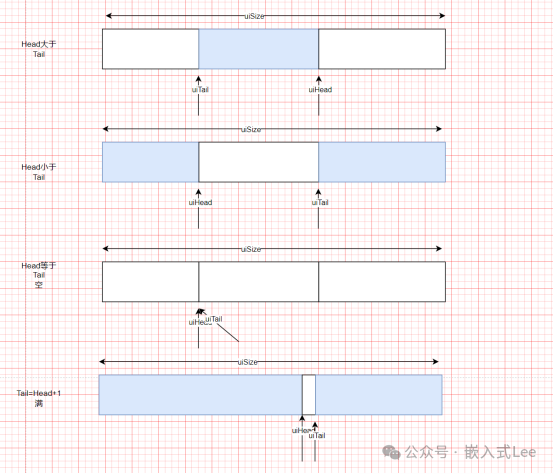
缓存原理如下所示,
4
种状态,阴影部分表示有效数据,
空时
Tail==Head
,
Tail=Head+1
时表示满
Head>Tail
时,有效数据大小是
Head-Tail,Tail
到
Head
部分是数据发送只需要直接发送这一块。
而空闲数据大小是
(uiBufferSize - uiHead - sizeof(uint32_t)) + uiTail
,即
- sizeof(uint32_t)
是预留一个位置表示满,即写时
Tail
永远不能追上
Head
,要预留一个位置。
Tail>Head
时也包括
Tail=Head+1
时,需要先发送到末尾部分,再发送开头部分,有效数据大小即
uiBufferSize -Tail+Head
。空闲数据大小即
uiTail - uiHead - sizeof(uint32_t)
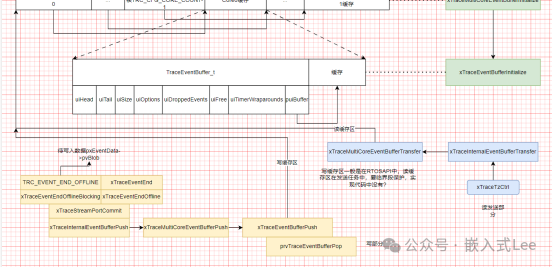
发送缓存的读写
前文提到了日志记录的操作模式如下
先
xTraceEventBegin
然后
TraceEventAddxxx
然后
xTraceEventEnd
其中
xTraceEventEnd
就是执行事件写入缓存的操作,最终对应的写缓存是函数
xTraceEventBufferPush
而任务 xTraceTzCtrl 中读缓存,最终对应是 xTraceMultiCoreEventBufferTransfer ->xTraceEventBufferTransfer 的实现
三.
读写发送缓存的实现
所以最终核心集中在写缓存
xTraceEventBufferPush
函数,读缓存
xTraceEventBufferTransfer
的实现上。
缓存区有以下几种状态
读写缓存,根据前面的系统框图分析,在不同的地方进行,那么必定涉及到资源临界段保护的问题。
临界段接口在
trcHardwarePort.h
中实现,一般是通过关开中断,或者是保存当前允许中断等级,设置当前允许中断等级,退出时恢复允许中断等级的方式实现。
比如我这里如下
extern uint32_t my_stream_get_tick(void);
其中写缓存
xTraceEventBufferPush
实际上层是
xTraceStreamPortCommit
,再上层是
xTraceEventEndOffline
,再上层即
xTraceEventEnd
xTraceEventEndOffline
实现如下,看到只有退出临界段的操作即
TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION
traceResult xTraceEventEndOffline(TraceEventHandle_t xEventHandle){TraceEventData_t* pxEventData = (TraceEventData_t*)xEventHandle;TraceCoreEventData_t* pxCoreEventData;int32_t iBytesCommitted;TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION()pxCoreEventData = &pxTraceEventDataTable->coreEventData[TRC_CFG_GET_CURRENT_CORE()];/* We restore the CORE specific variable to the local variable before any EXIT */TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION_NAME = pxCoreEventData->TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION_NAME;/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT_CUSTOM_ON_FAIL(xTraceIsComponentInitialized(TRC_RECORDER_COMPONENT_EVENT), TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(); return TRC_FAIL; );/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT_CUSTOM_ON_FAIL(pxEventData != 0, TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(); return TRC_FAIL; );/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT_CUSTOM_ON_FAIL(pxEventData->pvBlob != 0, TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(); return TRC_FAIL; );xTraceStreamPortCommit(pxEventData->pvBlob, pxEventData->size, &iBytesCommitted);/* We need to use iBytesCommitted for the above call but do not use the value,* remove potential warnings */(void)iBytesCommitted;RESET_EVENT_DATA(pxEventData);TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION();return TRC_SUCCESS;}
原来进入临界段操作是在
xTraceEventBegin->xTraceEventBeginOffline(即TRC_EVENT_BEGIN_OFFLINE)中调用xTraceEventBeginRawOffline进入的TRACE_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION();
traceResult xTraceEventBeginRawOffline(uint32_t uiSize, TraceEventHandle_t* pxEventHandle){TraceEventData_t* pxEventData;TraceCoreEventData_t* pxCoreEventData;int32_t ISR_nesting;TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION();/* We need to check this */if (!xTraceIsComponentInitialized(TRC_RECORDER_COMPONENT_EVENT)){return TRC_FAIL;}/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(pxEventHandle != 0);TRACE_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION();pxCoreEventData = &pxTraceEventDataTable->coreEventData[TRC_CFG_GET_CURRENT_CORE()];/* We backup the local variable to the CORE specific variable */pxCoreEventData->TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION_NAME = TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION_NAME;xTraceISRGetCurrentNesting(&ISR_nesting);/* We add 1 since xTraceISRGetCurrentNesting(...) returns -1 if no ISR is active */pxEventData = &pxCoreEventData->eventData[ISR_nesting + 1];/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT_CUSTOM_ON_FAIL(pxEventData->pvBlob == 0, TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(); return TRC_FAIL; );VERIFY_EVENT_SIZE(uiSize);pxEventData->size = ((uiSize + (sizeof(uint32_t) - 1)) / sizeof(uint32_t)) * sizeof(uint32_t); /* 4-byte align */pxEventData->offset = 0;/* This can fail and we should handle it */if (xTraceStreamPortAllocate(pxEventData->size, &pxEventData->pvBlob) == TRC_FAIL){TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION();return TRC_FAIL;}*pxEventHandle = (TraceEventHandle_t)pxEventData;return TRC_SUCCESS;}
因为实际以下过程是一个整体
先
xTraceEventBegin
然后
TraceEventAddxxx
然后
xTraceEventEnd
所以对上述过程简化下就如下,整个过程对操作发送缓存是临界段保护的
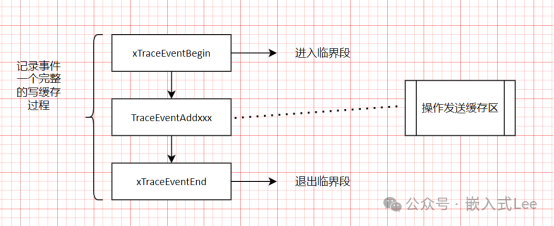
其中写缓存关键函数就是
xTraceEventBufferPush
它外面已经包含在临界段区里面了所以这个函数里面就不需要临界段处理了。
因此这个函数也不能阻塞。
因为临界段处理很多都是通过关中断实现的。
这里实现了两种模式,一种是满跳过,一种是满覆盖则先要弹出空间
prvTraceEventBufferPop再写入新的数据
traceResult xTraceEventBufferPush(TraceEventBuffer_t *pxTraceEventBuffer, void *pxData, uint32_t uiDataSize, int32_t *piBytesWritten){uint32_t uiBufferSize;/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(pxTraceEventBuffer != 0);/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(pxData != 0);uiBufferSize = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiSize;/* Check if the data size is larger than the buffer *//* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(uiDataSize <= uiBufferSize);/* Check byte alignment *//* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT((uiDataSize % 4) == 0);/* Ensure bytes written start at 0 *//* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(piBytesWritten != 0);*piBytesWritten = 0;/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT_ALWAYS_EVALUATE(xTraceTimestampGetWraparounds(&pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTimerWraparounds) == TRC_SUCCESS);/* In ring buffer mode we cannot provide lock free access since the producer modified* the head and tail variables in the same call. This option is only safe when used* with an internal buffer (streaming snapshot) which no consumer accesses.*/switch (pxTraceEventBuffer->uiOptions){case TRC_EVENT_BUFFER_OPTION_OVERWRITE:{uint32_t uiHead = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead;/* If there isn't enough space in the buffer pop events until there is */while (pxTraceEventBuffer->uiFree < uiDataSize){prvTraceEventBufferPop(pxTraceEventBuffer);}/* Copy data */if ((uiBufferSize - uiHead) > uiDataSize){TRC_MEMCPY(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiHead], pxData, uiDataSize);}else{TRC_MEMCPY(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiHead], pxData, uiBufferSize - uiHead);TRC_MEMCPY(pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer,(void*)(&((uint8_t*)pxData)[(uiBufferSize - uiHead)]),uiDataSize - (uiBufferSize - uiHead));}pxTraceEventBuffer->uiFree -= uiDataSize;pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead = (uiHead + uiDataSize) % uiBufferSize;*piBytesWritten = uiDataSize;break;}case TRC_EVENT_BUFFER_OPTION_SKIP:{/* Since a consumer could potentially update tail (free) during the procedure* we have to save it here to avoid problems with the push algorithm.*/uint32_t uiHead = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead;uint32_t uiTail = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail;if (uiHead >= uiTail){uint32_t uiFreeSpace = (uiBufferSize - uiHead - sizeof(uint32_t)) + uiTail;if (uiFreeSpace < uiDataSize){*piBytesWritten = 0;return TRC_SUCCESS;}/* Copy data */if ((uiBufferSize - uiHead) > uiDataSize){TRC_MEMCPY(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead], pxData, uiDataSize);}else{TRC_MEMCPY(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiHead], pxData, uiBufferSize - uiHead);TRC_MEMCPY(pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer,(void*)(&((uint8_t*)pxData)[(uiBufferSize - uiHead)]),uiDataSize - (uiBufferSize - uiHead));}pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead = (uiHead + uiDataSize) % uiBufferSize;}else{uint32_t uiFreeSpace = uiTail - uiHead - sizeof(uint32_t);if (uiFreeSpace < uiDataSize){*piBytesWritten = 0;return TRC_SUCCESS;}/* Copy data */TRC_MEMCPY(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead], pxData, uiDataSize);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead = (uiHead + uiDataSize);}*piBytesWritten = uiDataSize;break;}default:{return TRC_FAIL;}}return TRC_SUCCESS;}
再来看读缓存区的实现
xTraceEventBufferTransfer
,这个函数完全没有临界段保护,上一层也没有,所以这里是不对的,有比较严重的
BUG
。会导致缓存操作异常。
所以这里需要改为操作缓存时在临界段中进行,但是临界段可能是通过关闭中断实现的,发送接口
xTraceStreamPortWriteData
可能需要中断流式发送,所以
xTraceStreamPortWriteData
不能包含在临界段中,所以一个解决方法是,使用临时缓存,每次处理一个缓存。
原代码如下
traceResult xTraceEventBufferTransfer(TraceEventBuffer_t* pxTraceEventBuffer, int32_t* piBytesWritten){int32_t iBytesWritten = 0;int32_t iSumBytesWritten = 0;uint32_t uiHead;uint32_t uiTail;/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(pxTraceEventBuffer != 0);/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(piBytesWritten != 0);uiHead = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead;uiTail = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail;/* Check if core event buffer is empty */if (uiHead == uiTail){return TRC_SUCCESS;}/* Check if we can do a direct write or if we have to handle wrapping */if (uiHead > uiTail){xTraceStreamPortWriteData(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiTail], (uiHead - uiTail), &iBytesWritten);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail = uiHead;}else{xTraceStreamPortWriteData(&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiTail], (pxTraceEventBuffer->uiSize - uiTail), &iBytesWritten);iSumBytesWritten += iBytesWritten;xTraceStreamPortWriteData(pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer, uiHead, &iBytesWritten);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail = uiHead;}iSumBytesWritten += iBytesWritten;*piBytesWritten = iSumBytesWritten;return TRC_SUCCESS;}
最终实现如下
traceResult xTraceEventBufferTransfer(TraceEventBuffer_t* pxTraceEventBuffer, int32_t* piBytesWritten){#define SBUFFER_SIZE 1024static uint8_t sbuffer[SBUFFER_SIZE]; /* xTraceStreamPortWriteData一次发送的缓存 */int32_t iBytesWritten = 0;int32_t iSumBytesWritten = 0;uint32_t uiHead;uint32_t uiTail;uint32_t sendsize;/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(pxTraceEventBuffer != 0);/* This should never fail */TRC_ASSERT(piBytesWritten != 0);do{TRACE_ALLOC_CRITICAL_SECTION();TRACE_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(); /* 所有缓存相关的操作必须位于临界段保护下 */uiHead = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiHead;uiTail = pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail;/* Check if core event buffer is empty */if (uiHead == uiTail){TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION();return TRC_SUCCESS;}/* Check if we can do a direct write or if we have to handle wrapping */if (uiHead > uiTail){/* 如果读写指针未套圈* 待发送数据大于临时缓存,则先发临时缓存大小* 否则全部发送*/if((uiHead - uiTail) > SBUFFER_SIZE){TRC_MEMCPY(sbuffer,&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiTail],SBUFFER_SIZE);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail += SBUFFER_SIZE;//pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail %= pxTraceEventBuffer->uiSize;TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(); /* xTraceStreamPortWriteData位于临界段保护之外,此时缓存已经搬运到sbuffer */xTraceStreamPortWriteData(sbuffer, SBUFFER_SIZE, &iBytesWritten);}else{sendsize = (uiHead - uiTail);TRC_MEMCPY(sbuffer,&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiTail],sendsize);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail = uiHead;TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION();xTraceStreamPortWriteData(sbuffer, sendsize, &iBytesWritten);}}else{/* 如果读写指针套圈* 则先发送Tail到结束部分,下一次继续,就是未套圈的情形了* 待发送数据大于临时缓存,则先发临时缓存大小* 否则全部发送*/if((pxTraceEventBuffer->uiSize - uiTail) > SBUFFER_SIZE){TRC_MEMCPY(sbuffer,&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiTail],SBUFFER_SIZE);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail += SBUFFER_SIZE;TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION();xTraceStreamPortWriteData(sbuffer, SBUFFER_SIZE, &iBytesWritten);}else{sendsize = (pxTraceEventBuffer->uiSize - uiTail);TRC_MEMCPY(sbuffer,&pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer[uiTail],sendsize);pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail = 0;//pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail %= pxTraceEventBuffer->uiSize;TRACE_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION();xTraceStreamPortWriteData(sbuffer, sendsize, &iBytesWritten);}//xTraceStreamPortWriteData(pxTraceEventBuffer->puiBuffer, uiHead, &iBytesWritten);//pxTraceEventBuffer->uiTail = uiHead;}iSumBytesWritten += iBytesWritten;*piBytesWritten = iSumBytesWritten;}while(1);return TRC_SUCCESS;}
四.
总结
官方代码,在写缓存时有临界段保护,读时无临界段保护,所以有严重
BUG
,实际测试也确实发现经常通讯异常,甚至程序挂掉。按照上述修改测试之后非常稳定了。现在环境稳定了,后面就可以开始各种实践应用了,比如栈使用的跟踪等。




